主要内容
搜索
Exciting news for students! 🚀Simulink Student Challenge 2023 is live! Unleash your engineering skills and compete for exciting rewards. Submission deadline is December 12th, 2023!
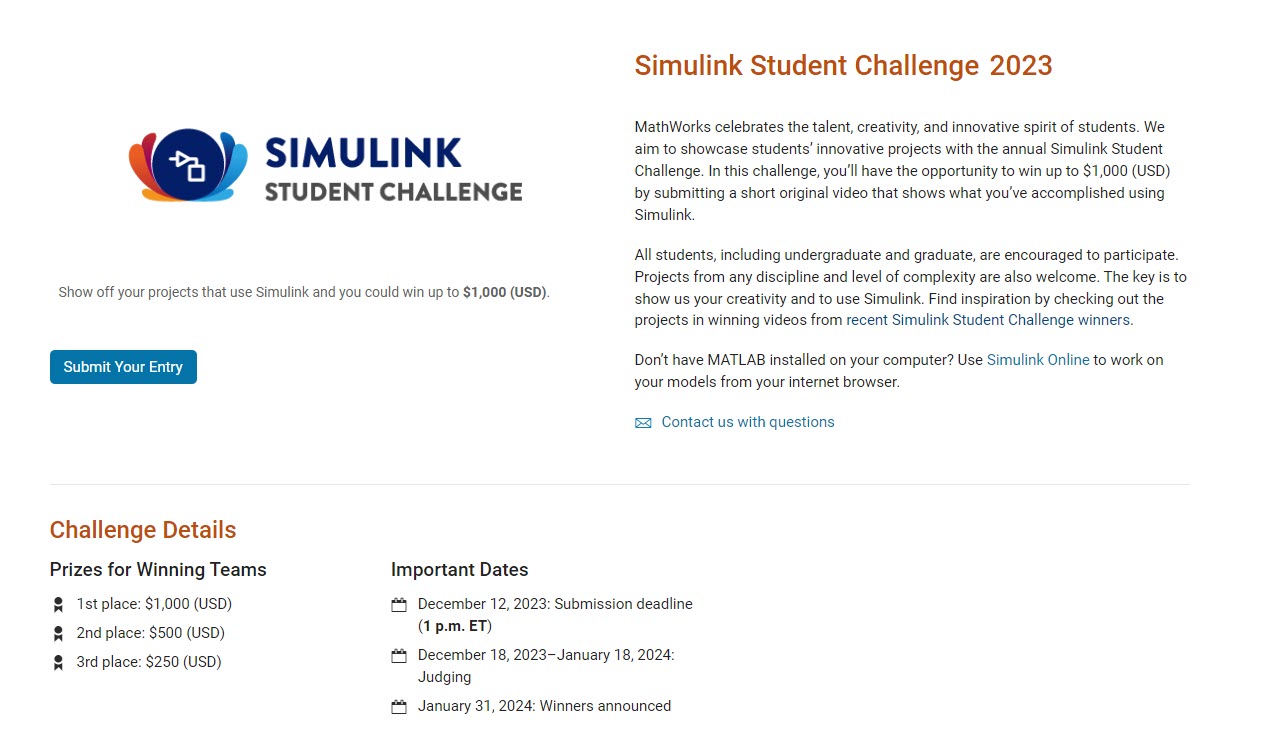
Simulink Student Challenge 2023
Enter the annual Simulink Student Challenge and demonstrate your creativity and engineering skills using Simulink. You could win $1,000 (USD).
In the past year, we've witnessed an exponential growth of ChatGPT and other Generative AI tools. AI has quickly become a transformative force across industries, from tech giants to small startups, and even community sites like ours. For instance, Stack Overflow announced its plan to leverage AI tools to draft a question or tag content; Quora built a ChatGPT bot to answer questions; and GitHub is piloting the AI tool for personalized content.
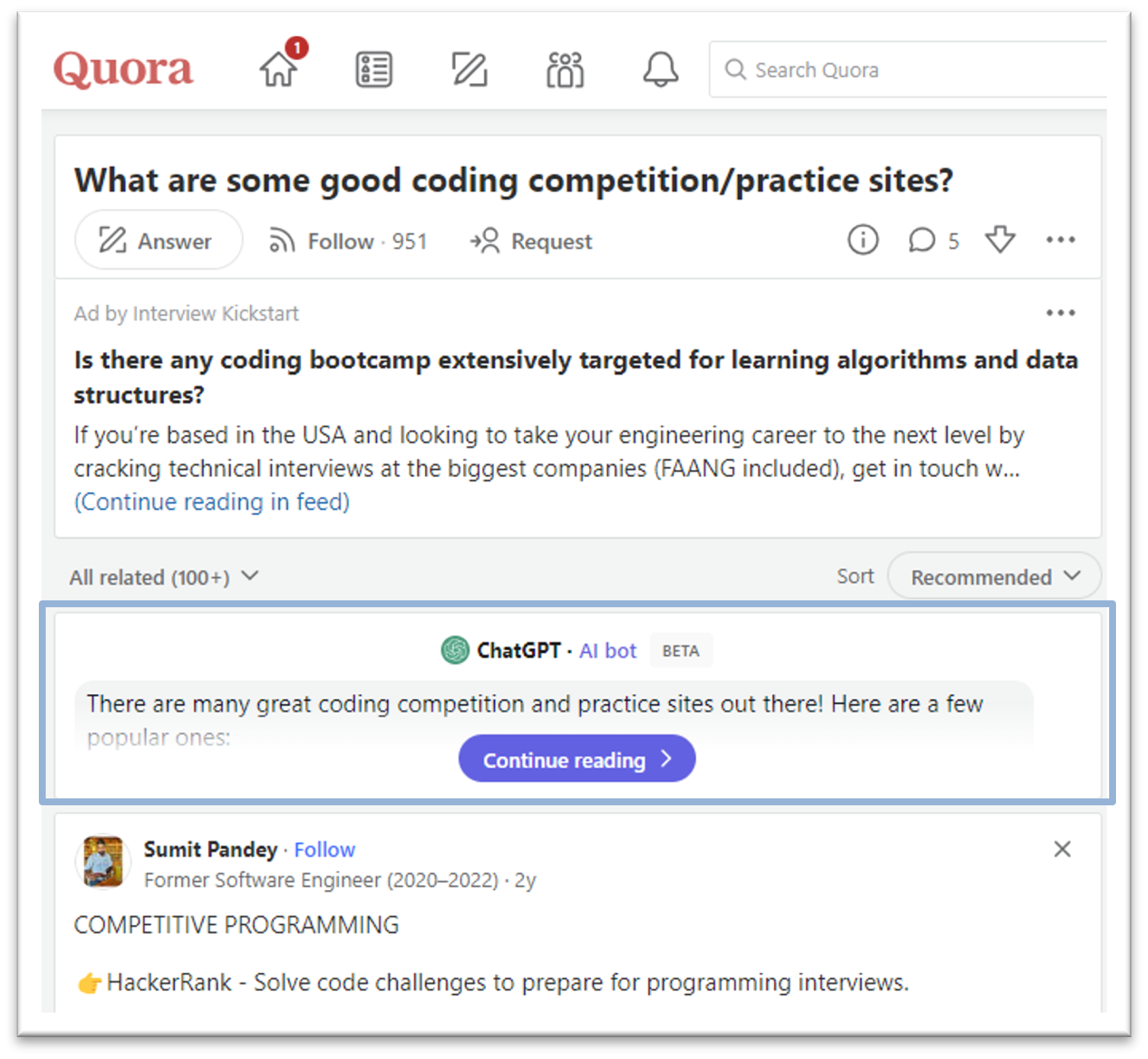
This trend in the community landscape makes me wonder what MATLAB Central community, especially in MATLAB Answers, can do to integrate AI and enhance the community.
Share with us your ideas in the comment session. Ideally one comment per idea, so that others can vote on a secific idea or have deeper discussions about it.
We launched the Discussions area with 6 channels, based on the existing types of content we see today in the MATLAB Central community.
I'm curious which channels you are most interested in participating, or which channels are missing.
Tell us your thoughts here!
Over the weekend I came across a pi approximation using durations of years and weeks (image below, Wolfram, eq. 89), accurate to 6 digits using the average Gregorian year (365.2425 days).
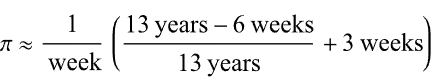
Here it is in MATLAB. I divided by 1 week at the end rather than multiplying by its reciprocal because you can’t divide a numeric by a duration in MATLAB (1/week).
weeks = @(n)n*days(7);
piApprox = ((years(13)-weeks(6))/years(13) + weeks(3)) / weeks(1)
% piApprox = 3.141593493469302
Here’s a breakdown
- The first argument becomes 12.885 yrs / 13 yrs or 0.99115
- Add three weeks: 0.99115 + 3 weeks = 21.991 days
- The reduced fraction becomes 21.991 days / 7 days
Now it looks a lot closer to the more familiar approximation for pi 22/7 but with greater precision!
This person used computer version to build a keyboard input, and used standard flag semaphore for the positions.
Flag semaphore is used mostly by sailors to be able to communicate optically over a distance; it does not need anything more than make-shift flags (but binoculars or telescopes can help.) Trained users can go faster than you might guess.
Chen, Rena, and I are at a community management event. It's great to be with others talking about relationships, trust, and co-creation.
A research team found a way to trick a number of AI systems by injecting carefully placed nonsense -- for example being able able to beat DeepMind's Go game.
This video discusses the "Cody" bridge, which is a pedestrian bridge over a canal that has been designed to move up and out of the way when ships need to travel through. The mathematics of the bridge movement are discussed and diagrammed. It is unique and educational.
Recently developed: a "microscope" based on touch and stereo vision.
Using touch removes the possibility of optical confusion -- for example, black on touch is only due to shape, not due to the possibility that the object has a black patch.
Sorry, you might need a Facebook account to watch the video.
I'm curious how the community uses the hold command when creating charts and graphics in MATLAB. In short, hold on sets up the axes to add new objects to the axes while hold off sets up the axes to reset when new objects are added.
When you use hold on do you always follow up with hold off? What's your reasoning on this decision?
Can't wait to discuss this here! I'd love to hear from newbies and experts alike!
Calling all students! New to MATLAB or need helpful resources? Check out our MATLAB GitHub for Students repository! Find MATLAB examples, videos, cheat sheets, and more!
Visit the repository here: MATLAB GitHub for Students
Imagine x is a large vector and you want the smallest 10 elements. How might you do it?

The way we've solved ODEs in MATLAB has been relatively unchanged at the user-level for decades. Indeed, I consider ode45 to be as iconic as backslash! There have been a few new solvers in recent years -- ode78 and ode89 for example -- and various things have gotten much faster but if you learned how to solve ODEs in MATLAB in 1997 then your knowledge is still applicable today.
In R2023b, there's a completely new framework for solving ODEs and I love it! You might argue that I'm contractually obliged to love it since I'm a MathWorker but I can assure you this is the real thing!
I wrote it up in a tutorial style on The MATLAB Blog https://blogs.mathworks.com/matlab/2023/10/03/the-new-solution-framework-for-ordinary-differential-equations-odes-in-matlab-r2023b/
The new interface makes a lot of things a much easier to do. Its also setting us up for a future where we'll be able to do some very cool algorithmic stuff behind the scenes.
Let me know what you think of the new functionality and what you think MathWorks should be doing next in the area of ODEs.
The new solution framework for Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) in MATLAB R2023b
Along with linear algebra, one of the iconic features of MATLAB in my mind is how it handles ordinary differential equations (ODEs). ODEs have been part of MATLAB almost since the very beginning.One of the features of how MATLAB traditionally allows users to solve ODEs is that it provides a suite of functions. For many years, there were 7
To solve the puzzle, first unscramble each of the words on the left. Then rearrange the letters in the yellow shaded boxes to complete the sentence on the right.

If you enjoyed this puzzle let me know with a like or in the comments below and I'll post more of them. Please don't post your answer, or any hints, and spoil it for those who come across this puzzle after you!! If you want to check your answer, you can messge me your guess through the link on my profile card (click on my name, Rena Berman, above and then on the envelope icon in the top right corner of the profile card that appears).
Thats the task:
Given a square cell array:
x = {'01', '56'; '234', '789'};
return a single character array:
y = '0123456789'
I wrote a code that passes Test 1 and 2 and one that passes Test 3 but I'm searching a condition so that the code for Test 3 runs when the cell array only contains letters and the one for Test 1 and 2 in every other case. Can somebody help me?
This is my code:
y = []
[a,b]=size(x)
%%TEST 3
delimiter=zeros(1,a)
delimiter(end)=1
delimiter=repmat(delimiter,1,b)
delimiter(end)=''
delimiter=string(delimiter)
y=[]
for i=1:a*b
y = string([y x(i)])
end
y=join(y,delimiter)
y=erase(y,'0')
y=regexprep(y,'1',' ')
%%TEST 1+2
for i=1:a*b
y = string([y x(i)])
y=join(y)
end
y=erase(y,' ' )
That's the question: Given four different positive numbers, a, b, c and d, provided in increasing order: a < b < c < d, find if any three of them comprise sides of a right-angled triangle. Return true if they do, otherwise return false .
I wrote this code but it doesn't pass test 7. I don't really understand why it isn't working. Can somebody help me?
function flag = isTherePythagoreanTriple(a, b, c, d)
a2=a^2
b2=b^2
c2=c^2
d2=d^2
format shortG
if a2+b2==c2
flag=true
else if a2+b2==d2
flag=true
else if a2+c2==d2
flag=true
else if c2+b2==d2
flag=true
else flag=false
end
end
end
end
end
That's the question:
The file cars.mat contains a table named cars with variables Model, MPG, Horsepower, Weight, and Acceleration for several classic cars.
Load the MAT-file. Given an integer N, calculate the output variable mpg.
Output mpg should contain the MPG of the top N lightest cars (by Weight) in a column vector.
I wrote this code and the resulting column vector has the right values but it doesn't pass the tests. What's wrong?
function mpg = sort_cars(N)
load cars.mat
sorted=sortrows(cars,4)
mpg = sorted(1:N,2)
end