主要内容
搜索
Imagine that the earth is a perfect sphere with a radius of 6371000 meters and there is a rope tightly wrapped around the equator. With one line of MATLAB code determine how much the rope will be lifted above the surface if you cut it and insert a 1 meter segment of rope into it (and then expand the whole rope back into a circle again, of course).
A library of runnable PDEs. See the equations! Modify the parameters! Visualize the resulting system in your browser! Convenient, fast, and instructive.
hello i found the following tools helpful to write matlab programs. copilot.microsoft.com chatgpt.com/gpts gemini.google.com and ai.meta.com. thanks a lot and best wishes.
Hi everyone,
I've recently joined a forest protection team in Greece, where we use drones for various tasks. This has sparked my interest in drone programming, and I'd like to learn more about it. Can anyone recommend any beginner-friendly courses or programs that teach drone programming?
I'm particularly interested in courses that focus on practical applications and might align with the work we do in forest protection. Any suggestions or guidance would be greatly appreciated!
Thank you!
"What are your favorite features or functionalities in MATLAB, and how have they positively impacted your projects or research? Any tips or tricks to share?
Check out the LLMs with MATLAB project on File Exchange to access Large Language Models from MATLAB.
Along with the latest support for GPT-4o mini, you can use LLMs with MATLAB to generate images, categorize data, and provide semantic analyis.
Something that had bothered me ever since I became an FEA analyst (2012) was the apparent inability of the "camera" in Matlab's 3D plot to function like the "cameras" in CAD/CAE packages.
For instance, load the ForearmLink.stl model that ships with the PDE Toolbox in Matlab and ParaView and try rotating the model.
clear
close all
gm = importGeometry( "ForearmLink.stl" );
pdegplot(gm)
Things to observe:
- Note that I cant seem to rotate continuously around the x-axis. It appears to only support rotations from [0, 360] as opposed to [-inf, inf]. So, for example, if I'm looking in the Y+ direction and rotate around X so that I'm looking at the Z- direction, and then want to look in the Y- direction, I can't simply keep rotating around the X axis... instead have to rotate 180 degrees around the Z axis and then around the X axis. I'm not aware of any data visualization applications (e.g., ParaView, VisIt, EnSight) or CAD/CAE tools with such an interaction.
- Note that at the 50 second mark, I set a view in ParaView: looking in the [X-, Y-, Z-] direction with Y+ up. Try as I might in Matlab, I'm unable to achieve that same view perspective.
Today I discovered that if one turns on the Camera Toolbar from the View menubar, then clicks the Orbit Camera icon, then the No Principal Axis icon:
That then it acts in the manner I've long desired. Oh, and also, for the interested, it is programmatically available: https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/cameratoolbar.html
I might humbly propose this mode either be made more discoverable, similar to the little interaction widgets that pop up in figures:
Or maybe use the middle-mouse button to temporarily use this mode (a mouse setting in, e.g., Abaqus/CAE).
I've noticed is that the highly rated fonts for coding (e.g. Fira Code, Inconsolata, etc.) seem to overlook one issue that is key for coding in Matlab. While these fonts make 0 and O, as well as the 1 and l easily distinguishable, the brackets are not. Quite often the curly bracket looks similar to the curved bracket, which can lead to mistakes when coding or reviewing code.
So I was thinking: Could Mathworks put together a team to review good programming fonts, and come up with their own custom font designed specifically and optimized for Matlab syntax?
An option for 10th degree polynomials but no weighted linear least squares. Seriously? Jesse
What do you think about the NVIDIA's achivement of becoming the top giant of manufacturing chips, especially for AI world?

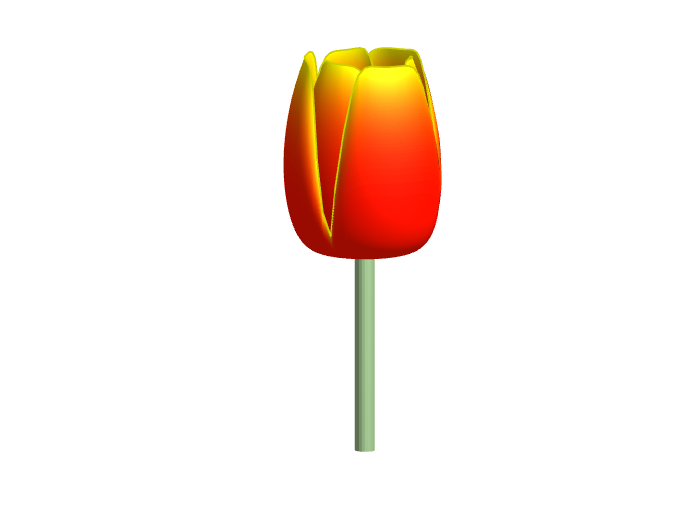
Spring is here in Natick and the tulips are blooming! While tulips appear only briefly here in Massachusetts, they provide a lot of bright and diverse colors and shapes. To celebrate this cheerful flower, here's some code to create your own tulip!

One of the starter prompts is about rolling two six-sided dice and plot the results. As a hobby, I create my own board games. I was able to use the dice rolling prompt to show how a simple roll and move game would work. That was a great surprise!
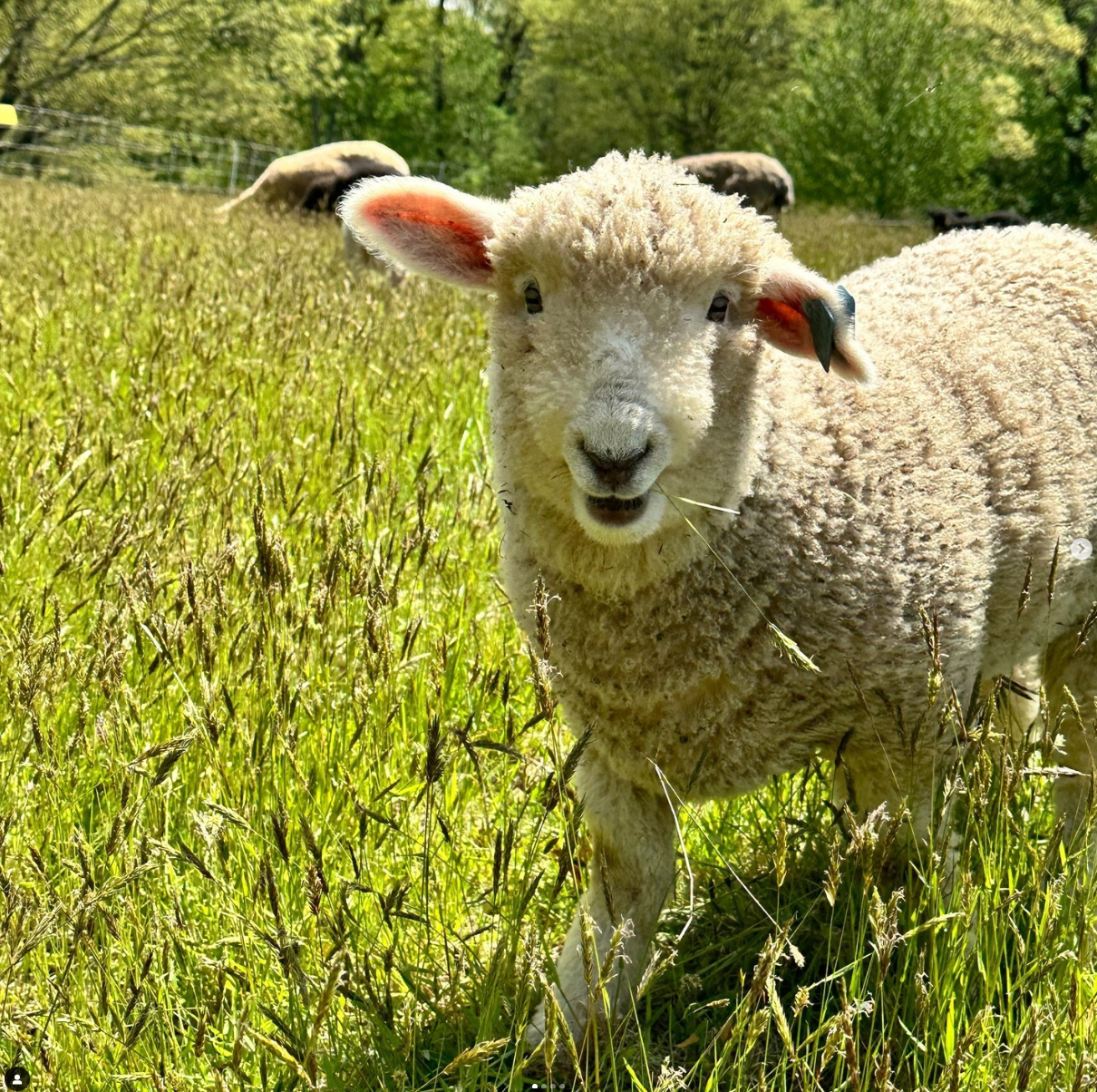
Drumlin Farm has welcomed MATLAMB, named in honor of MathWorks, among ten adorable new lambs this season!

I found this plot of words said by different characters on the US version of The Office sitcom. There's a sparkline for each character from pilot to finale episode.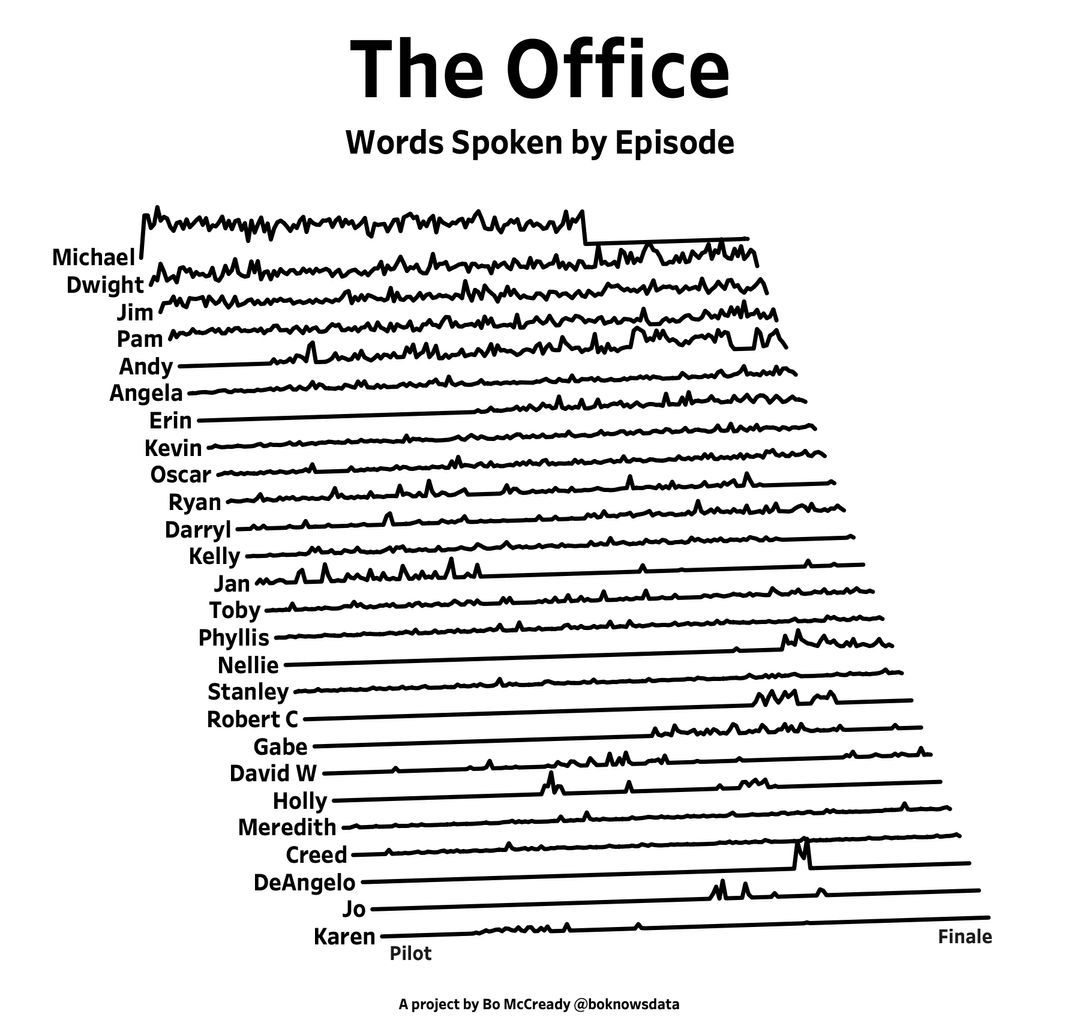

A high school student called for help with this physics problem:
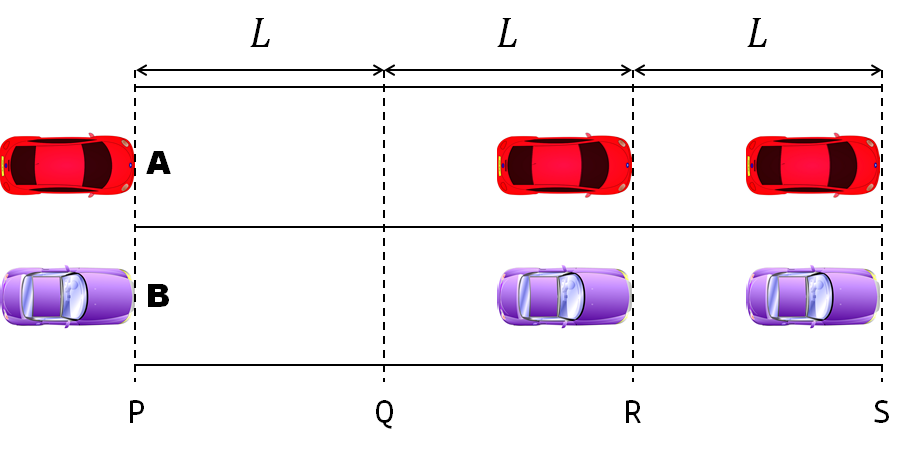
- Car A moves with constant velocity v.
- Car B starts to move when Car A passes through the point P.
- Car B undergoes...
- uniform acc. motion from P to Q.
- uniform velocity motion from Q to R.
- uniform acc. motion from R to S.
- Car A and B pass through the point R simultaneously.
- Car A and B arrive at the point S simultaneously.
Q1. When car A passes the point Q, which is moving faster?
Q2. Solve the time duration for car B to move from P to Q using L and v.
Q3. Magnitude of acc. of car B from P to Q, and from R to S: which is bigger?
Well, it can be solved with a series of tedious equations. But... how about this?
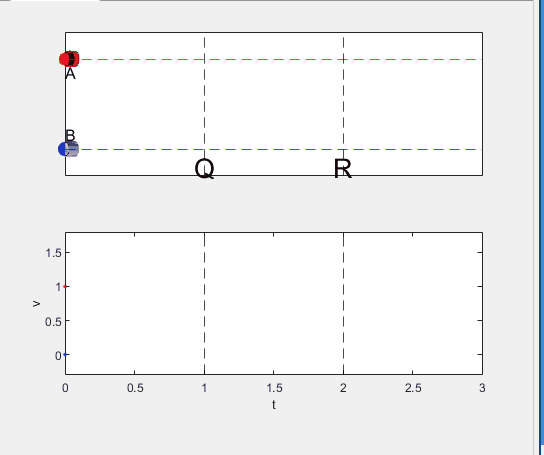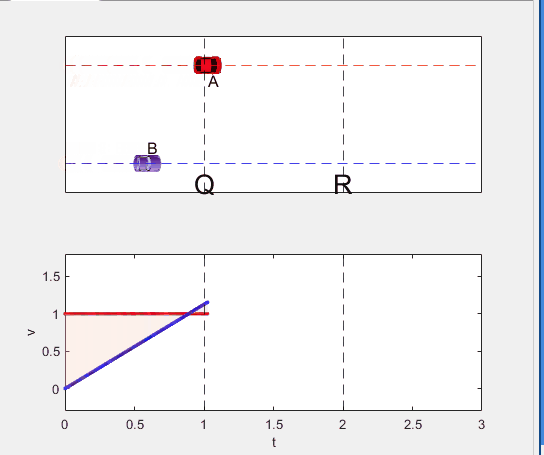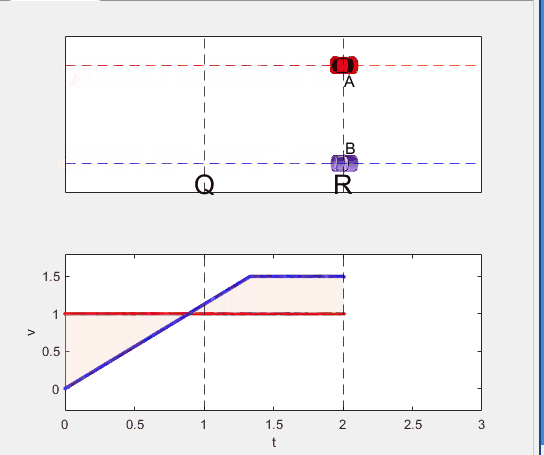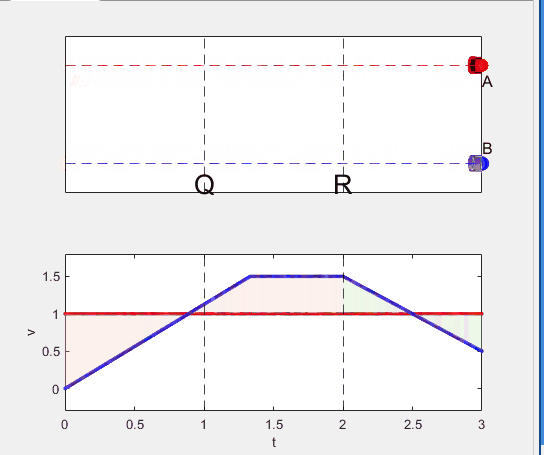
Code below:
%% get images and prepare stuffs
figure(WindowStyle="docked"),
ax1 = subplot(2,1,1);
hold on, box on
ax1.XTick = [];
ax1.YTick = [];
A = plot(0, 1, 'ro', MarkerSize=10, MarkerFaceColor='r');
B = plot(0, 0, 'bo', MarkerSize=10, MarkerFaceColor='b');
[carA, ~, alphaA] = imread('https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2013/07/12/11/58/car-145008_960_720.png');
[carB, ~, alphaB] = imread('https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2014/04/03/10/54/car-311712_960_720.png');
carA = imrotate(imresize(carA, 0.1), -90);
carB = imrotate(imresize(carB, 0.1), 180);
alphaA = imrotate(imresize(alphaA, 0.1), -90);
alphaB = imrotate(imresize(alphaB, 0.1), 180);
carA = imagesc(carA, AlphaData=alphaA, XData=[-0.1, 0.1], YData=[0.9, 1.1]);
carB = imagesc(carB, AlphaData=alphaB, XData=[-0.1, 0.1], YData=[-0.1, 0.1]);
txtA = text(0, 0.85, 'A', FontSize=12);
txtB = text(0, 0.17, 'B', FontSize=12);
yline(1, 'r--')
yline(0, 'b--')
xline(1, 'k--')
xline(2, 'k--')
text(1, -0.2, 'Q', FontSize=20, HorizontalAlignment='center')
text(2, -0.2, 'R', FontSize=20, HorizontalAlignment='center')
% legend('A', 'B') % this make the animation slow. why?
xlim([0, 3])
ylim([-.3, 1.3])
%% axes2: plots velocity graph
ax2 = subplot(2,1,2);
box on, hold on
xlabel('t'), ylabel('v')
vA = plot(0, 1, 'r.-');
vB = plot(0, 0, 'b.-');
xline(1, 'k--')
xline(2, 'k--')
xlim([0, 3])
ylim([-.3, 1.8])
p1 = patch([0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0], [248, 209, 188]/255, ...
EdgeColor = 'none', ...
FaceAlpha = 0.3);
%% solution
v = 1; % car A moves with constant speed.
L = 1; % distances of P-Q, Q-R, R-S
% acc. of car B for three intervals
a(1) = 9*v^2/8/L;
a(2) = 0;
a(3) = -1;
t_BatQ = sqrt(2*L/a(1)); % time when car B arrives at Q
v_B2 = a(1) * t_BatQ; % speed of car B between Q-R
%% patches for velocity graph
p2 = patch([t_BatQ, t_BatQ, t_BatQ, t_BatQ], [1, 1, v_B2, v_B2], ...
[248, 209, 188]/255, ...
EdgeColor = 'none', ...
FaceAlpha = 0.3);
p3 = patch([2, 2, 2, 2], [1, v_B2, v_B2, 1], [194, 234, 179]/255, ...
EdgeColor = 'none', ...
FaceAlpha = 0.3);
%% animation
tt = linspace(0, 3, 2000);
for t = tt
A.XData = v * t;
vA.XData = [vA.XData, t];
vA.YData = [vA.YData, 1];
if t < t_BatQ
B.XData = 1/2 * a(1) * t^2;
vB.XData = [vB.XData, t];
vB.YData = [vB.YData, a(1) * t];
p1.XData = [0, t, t, 0];
p1.YData = [0, vB.YData(end), 1, 1];
elseif t >= t_BatQ && t < 2
B.XData = L + (t - t_BatQ) * v_B2;
vB.XData = [vB.XData, t];
vB.YData = [vB.YData, v_B2];
p2.XData = [t_BatQ, t, t, t_BatQ];
p2.YData = [1, 1, vB.YData(end), vB.YData(end)];
else
B.XData = 2*L + v_B2 * (t - 2) + 1/2 * a(3) * (t-2)^2;
vB.XData = [vB.XData, t];
vB.YData = [vB.YData, v_B2 + a(3) * (t - 2)];
p3.XData = [2, t, t, 2];
p3.YData = [1, 1, vB.YData(end), v_B2];
end
txtA.Position(1) = A.XData(end);
txtB.Position(1) = B.XData(end);
carA.XData = A.XData(end) + [-.1, .1];
carB.XData = B.XData(end) + [-.1, .1];
drawnow
end
is there any sites available online free ai course learning except: coursera.org
Northern lights captured from this weekend at MathWorks campus ✨
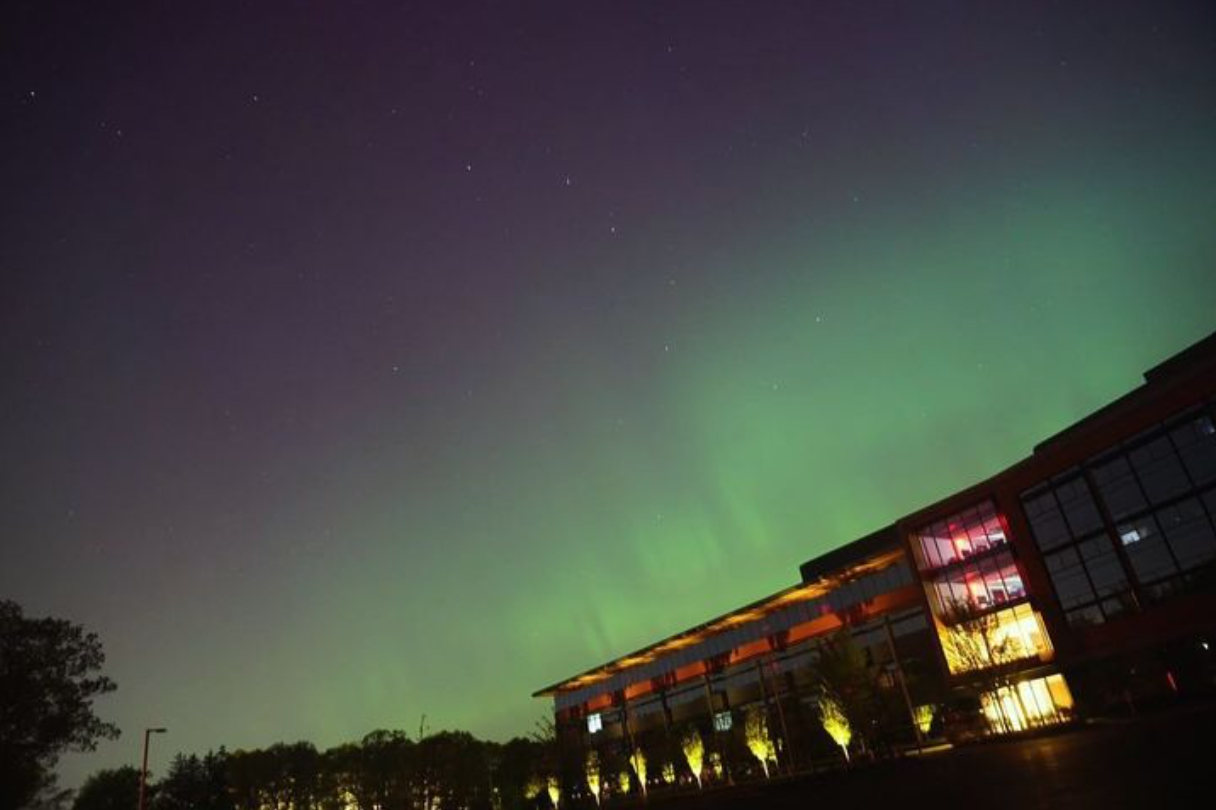

Did you get a chance to see lights and take some photos?
Dear MATLAB contest enthusiasts,
I believe many of you have been captivated by the innovative entries from Zhaoxu Liu / slanderer, in the 2023 MATLAB Flipbook Mini Hack contest.

Ever wondered about the person behind these creative entries? What drives a MATLAB user to such levels of skill? And what inspired his participation in the contest? We were just as curious as you are!
We were delighted to catch up with him and learn more about his use of MATLAB. The interview has recently been published in MathWorks Blogs. For an in-depth look into his insights and experiences, be sure to read our latest blog post: Community Q&A – Zhaoxu Liu.
But the conversation doesn't end here! Who would you like to see featured in our next interview? Drop their name in the comments section below and let us know who we should reach out to next!
Updating some of my educational Livescripts to 2024a, really love the new "define a function anywhere" feature, and have a "new" idea for improving Livescripts -- support "hidden" code blocks similar to the Jupyter Notebooks functionality.
For example, I often create "complicated" plots with a bunch of ancillary items and I don't want this code exposed to the reader by default, as it might confuse the reader. For example, consider a Livescript that might read like this:
-----
Noting the similar structure of these two mappings, let's now write a function that simply maps from some domain to some other domain using change of variable.
function x = ChangeOfVariable( x, from_domain, to_domain )
x = x - from_domain(1);
x = x * ( ( to_domain(2) - to_domain(1) ) / ( from_domain(2) - from_domain(1) ) );
x = x + to_domain(1);
end
Let's see this function in action
% HIDE CELL
clear
close all
from_domain = [-1, 1];
to_domain = [2, 7];
from_values = [-1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1];
to_values = ChangeOfVariable( from_values, from_domain, to_domain )
to_values = 1×5
2.0000 3.2500 4.5000 5.7500 7.0000
We can plot the values of from_values and to_values, showing how they're connected to each other:
% HIDE CELL
figure
hold on
for n = 1 : 5
plot( [from_values(n) to_values(n)], [1 0], Color="k", LineWidth=1 )
end
ax = gca;
ax.YTick = [];
ax.XLim = [ min( [from_domain, to_domain] ) - 1, max( [from_domain, to_domain] ) + 1 ];
ax.YLim = [-0.5, 1.5];
ax.XGrid = "on";
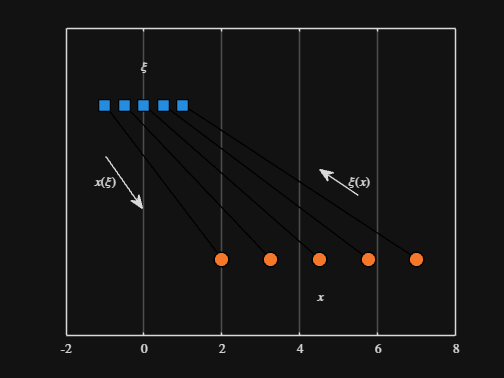
scatter( from_values, ones( 5, 1 ), Marker="s", MarkerFaceColor="flat", MarkerEdgeColor="k", SizeData=120, LineWidth=1, SeriesIndex=1 )
text( mean( from_domain ), 1.25, "$\xi$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
scatter( to_values, zeros( 5, 1 ), Marker="o", MarkerFaceColor="flat", MarkerEdgeColor="k", SizeData=120, LineWidth=1, SeriesIndex=2 )
text( mean( to_domain ), -0.25, "$x$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
scaled_arrow( ax, [mean( [from_domain(1), to_domain(1) ] ) - 1, 0.5], ( 1 - 0 ) / ( from_domain(1) - to_domain(1) ), 1 )
scaled_arrow( ax, [mean( [from_domain(end), to_domain(end)] ) + 1, 0.5], ( 1 - 0 ) / ( from_domain(end) - to_domain(end) ), -1 )
text( mean( [from_domain(1), to_domain(1) ] ) - 1.5, 0.5, "$x(\xi)$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
text( mean( [from_domain(end), to_domain(end)] ) + 1.5, 0.5, "$\xi(x)$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
-----
Where scaled_arrow is some utility function I've defined elsewhere... See how a majority of the code is simply "drivel" to create the plot, clear and close? I'd like to be able to hide those cells so that it would look more like this:
-----
Noting the similar structure of these two mappings, let's now write a function that simply maps from some domain to some other domain using change of variable.
function x = ChangeOfVariable( x, from_domain, to_domain )
x = x - from_domain(1);
x = x * ( ( to_domain(2) - to_domain(1) ) / ( from_domain(2) - from_domain(1) ) );
x = x + to_domain(1);
end
Let's see this function in action
▶ Show code cell
from_domain = [-1, 1];
to_domain = [2, 7];
from_values = [-1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1];
to_values = ChangeOfVariable( from_values, from_domain, to_domain )
to_values = 1×5
2.0000 3.2500 4.5000 5.7500 7.0000
We can plot the values of from_values and to_values, showing how they're connected to each other:
▶ Show code cell
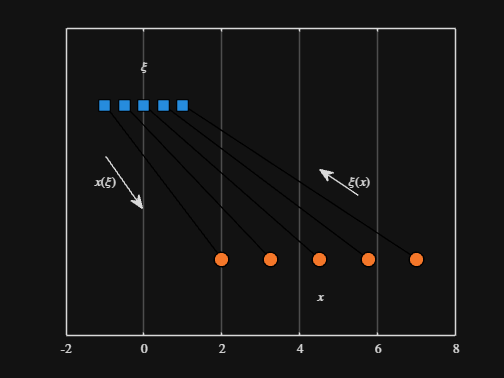
-----
Thoughts?
I recently had issues with code folding seeming to disappear and it turns out that I had unknowingly disabled the "show code folding margin" option by accident. Despite using MATLAB for several years, I had no idea this was an option, especially since there seemed to be no references to it in the code folding part of the "Preferences" menu.
It would be great if in the future, there was a warning that told you about this when you try enable/disable folding in the Preferences.
I am using 2023b by the way.

