主要内容
搜索
Don't use / What are Projects?
26%
1–10
31%
11–20
15%
21–30
9%
31–50
7%
51+ (comment below)
12%
4070 个投票
The study of the dynamics of the discrete Klein - Gordon equation (DKG) with friction is given by the equation :

above equation, W describes the potential function :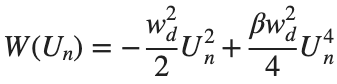
The objective of this simulation is to model the dynamics of a segment of DNA under thermal fluctuations with fixed boundaries using a modified discrete Klein-Gordon equation. The model incorporates elasticity, nonlinearity, and damping to provide insights into the mechanical behavior of DNA under various conditions.
% Parameters
numBases = 200; % Number of base pairs, representing a segment of DNA
kappa = 0.1; % Elasticity constant
omegaD = 0.2; % Frequency term
beta = 0.05; % Nonlinearity coefficient
delta = 0.01; % Damping coefficient
- Position: Random initial perturbations between 0.01 and 0.02 to simulate the thermal fluctuations at the start.
- Velocity: All bases start from rest, assuming no initial movement except for the thermal perturbations.
% Random initial perturbations to simulate thermal fluctuations
initialPositions = 0.01 + (0.02-0.01).*rand(numBases,1);
initialVelocities = zeros(numBases,1); % Assuming initial rest state
The simulation uses fixed ends to model the DNA segment being anchored at both ends, which is typical in experimental setups for studying DNA mechanics. The equations of motion for each base are derived from a modified discrete Klein-Gordon equation with the inclusion of damping:
% Define the differential equations
dt = 0.05; % Time step
tmax = 50; % Maximum time
tspan = 0:dt:tmax; % Time vector
x = zeros(numBases, length(tspan)); % Displacement matrix
x(:,1) = initialPositions; % Initial positions
% Velocity-Verlet algorithm for numerical integration
for i = 2:length(tspan)
% Compute acceleration for internal bases
acceleration = zeros(numBases,1);
for n = 2:numBases-1
acceleration(n) = kappa * (x(n+1, i-1) - 2 * x(n, i-1) + x(n-1, i-1)) ...
- delta * initialVelocities(n) - omegaD^2 * (x(n, i-1) - beta * x(n, i-1)^3);
end
% positions for internal bases
x(2:numBases-1, i) = x(2:numBases-1, i-1) + dt * initialVelocities(2:numBases-1) ...
+ 0.5 * dt^2 * acceleration(2:numBases-1);
% velocities using new accelerations
newAcceleration = zeros(numBases,1);
for n = 2:numBases-1
newAcceleration(n) = kappa * (x(n+1, i) - 2 * x(n, i) + x(n-1, i)) ...
- delta * initialVelocities(n) - omegaD^2 * (x(n, i) - beta * x(n, i)^3);
end
initialVelocities(2:numBases-1) = initialVelocities(2:numBases-1) + 0.5 * dt * (acceleration(2:numBases-1) + newAcceleration(2:numBases-1));
end
% Visualization of displacement over time for each base pair
figure;
hold on;
for n = 2:numBases-1
plot(tspan, x(n, :));
end
xlabel('Time');
ylabel('Displacement');
legend(arrayfun(@(n) ['Base ' num2str(n)], 2:numBases-1, 'UniformOutput', false));
title('Displacement of DNA Bases Over Time');
hold off;
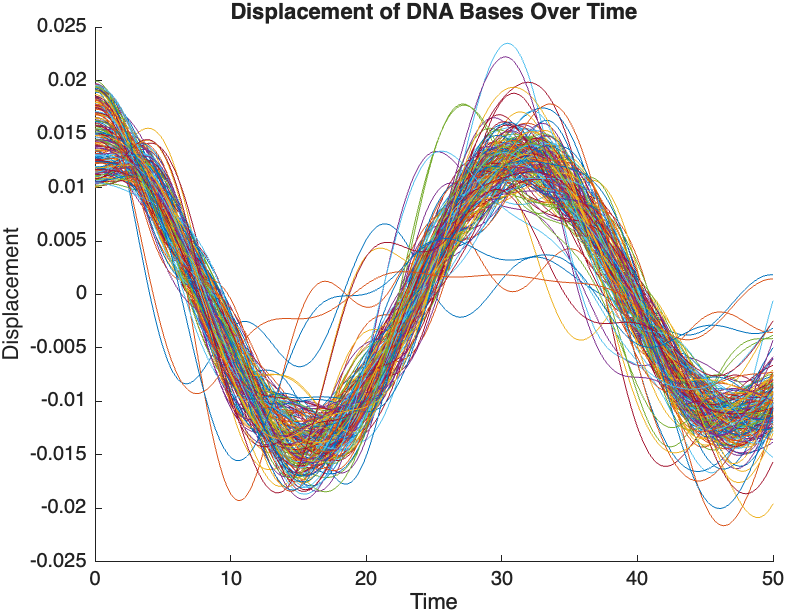
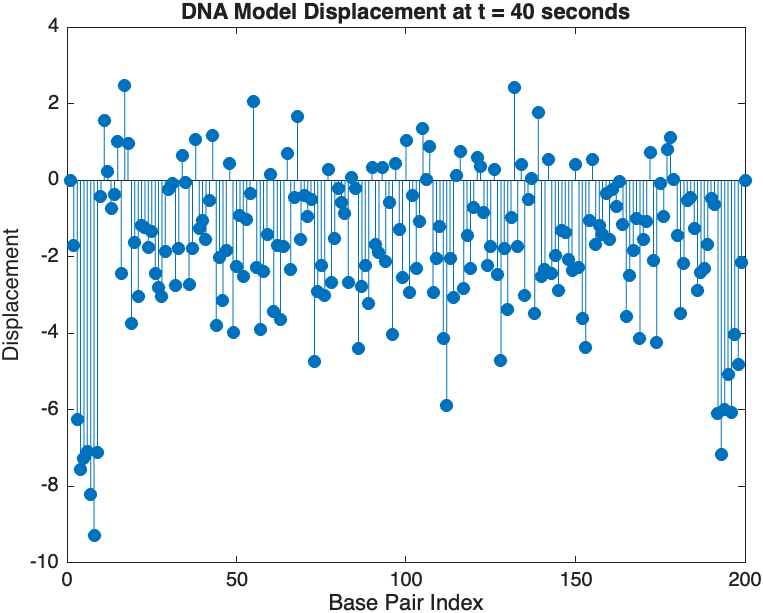
The results are visualized using a plot that shows the displacements of each base over time . Key observations from the simulation include :
- Wave Propagation: The initial perturbations lead to wave-like dynamics along the segment, with visible propagation and reflection at the boundaries.
- Damping Effects: The inclusion of damping leads to a gradual reduction in the amplitude of the oscillations, indicating energy dissipation over time.
- Nonlinear Behavior: The nonlinear term influences the response, potentially stabilizing the system against large displacements or leading to complex dynamic patterns.
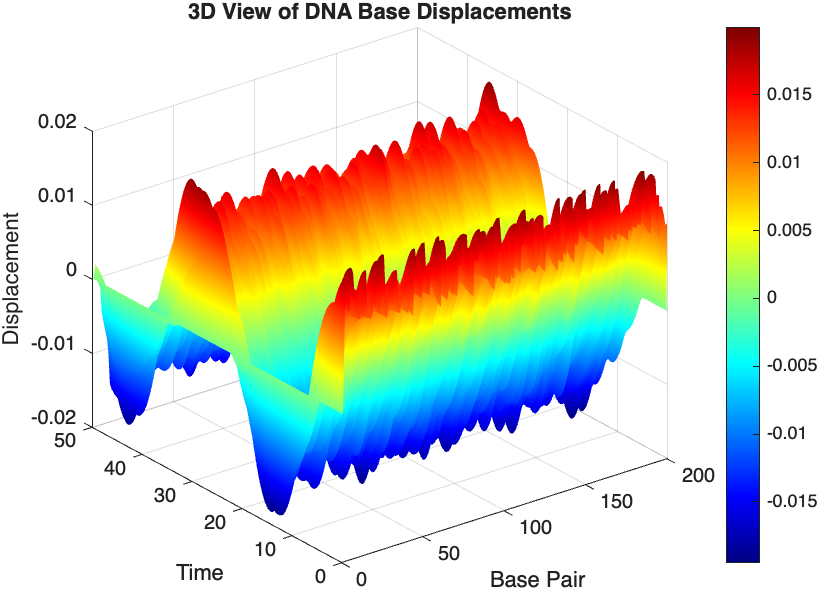
% 3D plot for displacement
figure;
[X, T] = meshgrid(1:numBases, tspan);
surf(X', T', x);
xlabel('Base Pair');
ylabel('Time');
zlabel('Displacement');
title('3D View of DNA Base Displacements');
colormap('jet');
shading interp;
colorbar; % Adds a color bar to indicate displacement magnitude
% Snapshot visualization at a specific time
snapshotTime = 40; % Desired time for the snapshot
[~, snapshotIndex] = min(abs(tspan - snapshotTime)); % Find closest index
snapshotSolution = x(:, snapshotIndex); % Extract displacement at the snapshot time
% Plotting the snapshot
figure;
stem(1:numBases, snapshotSolution, 'filled'); % Discrete plot using stem
title(sprintf('DNA Model Displacement at t = %d seconds', snapshotTime));
xlabel('Base Pair Index');
ylabel('Displacement');
% Time vector for detailed sampling
tDetailed = 0:0.5:50; % Detailed time steps
% Initialize an empty array to hold the data
data = [];
% Generate the data for 3D plotting
for i = 1:numBases
% Interpolate to get detailed solution data for each base pair
detailedSolution = interp1(tspan, x(i, :), tDetailed);
% Concatenate the current base pair's data to the main data array
data = [data; repmat(i, length(tDetailed), 1), tDetailed', detailedSolution'];
end
% 3D Plot
figure;
scatter3(data(:,1), data(:,2), data(:,3), 10, data(:,3), 'filled');
xlabel('Base Pair');
ylabel('Time');
zlabel('Displacement');
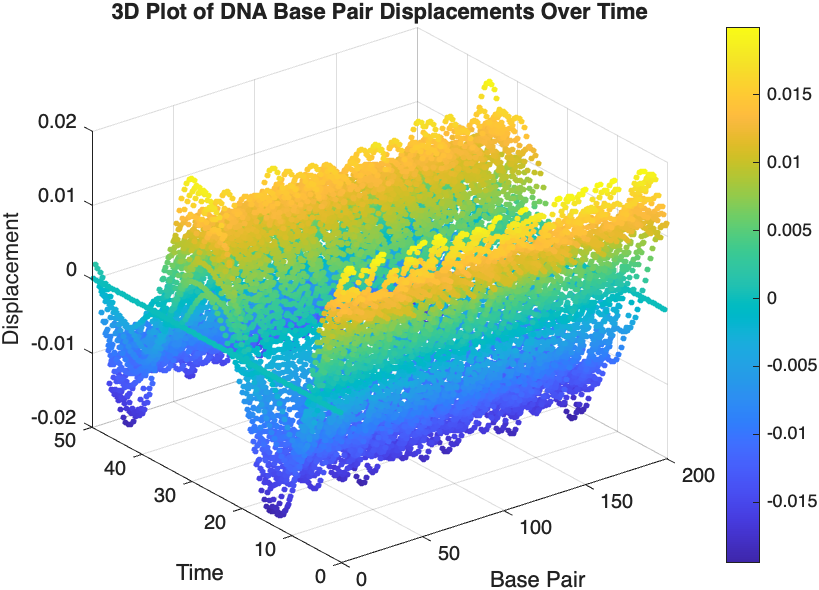
title('3D Plot of DNA Base Pair Displacements Over Time');
colorbar; % Adds a color bar to indicate displacement magnitude
Updating some of my educational Livescripts to 2024a, really love the new "define a function anywhere" feature, and have a "new" idea for improving Livescripts -- support "hidden" code blocks similar to the Jupyter Notebooks functionality.
For example, I often create "complicated" plots with a bunch of ancillary items and I don't want this code exposed to the reader by default, as it might confuse the reader. For example, consider a Livescript that might read like this:
-----
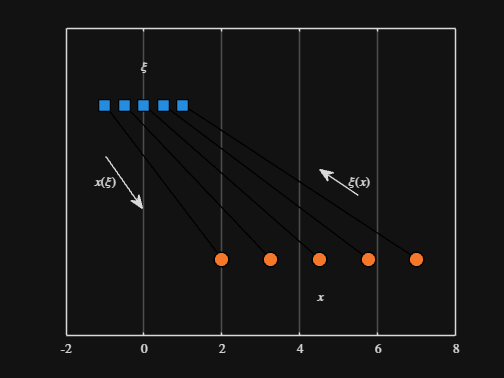
Noting the similar structure of these two mappings, let's now write a function that simply maps from some domain to some other domain using change of variable.
function x = ChangeOfVariable( x, from_domain, to_domain )
x = x - from_domain(1);
x = x * ( ( to_domain(2) - to_domain(1) ) / ( from_domain(2) - from_domain(1) ) );
x = x + to_domain(1);
end
Let's see this function in action
% HIDE CELL
clear
close all
from_domain = [-1, 1];
to_domain = [2, 7];
from_values = [-1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1];
to_values = ChangeOfVariable( from_values, from_domain, to_domain )
to_values = 1×5
2.0000 3.2500 4.5000 5.7500 7.0000
We can plot the values of from_values and to_values, showing how they're connected to each other:
% HIDE CELL
figure
hold on
for n = 1 : 5
plot( [from_values(n) to_values(n)], [1 0], Color="k", LineWidth=1 )
end
ax = gca;
ax.YTick = [];
ax.XLim = [ min( [from_domain, to_domain] ) - 1, max( [from_domain, to_domain] ) + 1 ];
ax.YLim = [-0.5, 1.5];
ax.XGrid = "on";
scatter( from_values, ones( 5, 1 ), Marker="s", MarkerFaceColor="flat", MarkerEdgeColor="k", SizeData=120, LineWidth=1, SeriesIndex=1 )
text( mean( from_domain ), 1.25, "$\xi$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
scatter( to_values, zeros( 5, 1 ), Marker="o", MarkerFaceColor="flat", MarkerEdgeColor="k", SizeData=120, LineWidth=1, SeriesIndex=2 )
text( mean( to_domain ), -0.25, "$x$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
scaled_arrow( ax, [mean( [from_domain(1), to_domain(1) ] ) - 1, 0.5], ( 1 - 0 ) / ( from_domain(1) - to_domain(1) ), 1 )
scaled_arrow( ax, [mean( [from_domain(end), to_domain(end)] ) + 1, 0.5], ( 1 - 0 ) / ( from_domain(end) - to_domain(end) ), -1 )
text( mean( [from_domain(1), to_domain(1) ] ) - 1.5, 0.5, "$x(\xi)$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
text( mean( [from_domain(end), to_domain(end)] ) + 1.5, 0.5, "$\xi(x)$", Interpreter="latex", HorizontalAlignment="center", VerticalAlignment="middle" )
-----
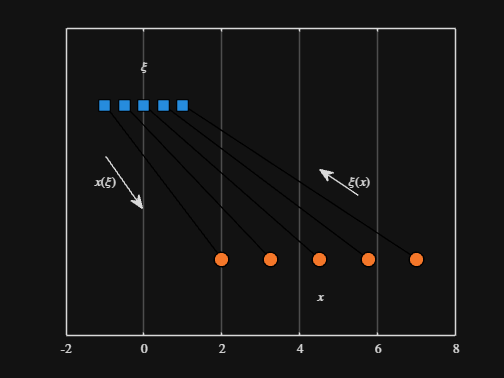
Where scaled_arrow is some utility function I've defined elsewhere... See how a majority of the code is simply "drivel" to create the plot, clear and close? I'd like to be able to hide those cells so that it would look more like this:
-----
Noting the similar structure of these two mappings, let's now write a function that simply maps from some domain to some other domain using change of variable.
function x = ChangeOfVariable( x, from_domain, to_domain )
x = x - from_domain(1);
x = x * ( ( to_domain(2) - to_domain(1) ) / ( from_domain(2) - from_domain(1) ) );
x = x + to_domain(1);
end
Let's see this function in action
▶ Show code cell
from_domain = [-1, 1];
to_domain = [2, 7];
from_values = [-1, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1];
to_values = ChangeOfVariable( from_values, from_domain, to_domain )
to_values = 1×5
2.0000 3.2500 4.5000 5.7500 7.0000
We can plot the values of from_values and to_values, showing how they're connected to each other:
▶ Show code cell
-----
Thoughts?
I recently had issues with code folding seeming to disappear and it turns out that I had unknowingly disabled the "show code folding margin" option by accident. Despite using MATLAB for several years, I had no idea this was an option, especially since there seemed to be no references to it in the code folding part of the "Preferences" menu.
It would be great if in the future, there was a warning that told you about this when you try enable/disable folding in the Preferences.
I am using 2023b by the way.
2
17%
3
12%
4
59%
6
4%
8
5%
Other (comment below)
3%
6419 个投票
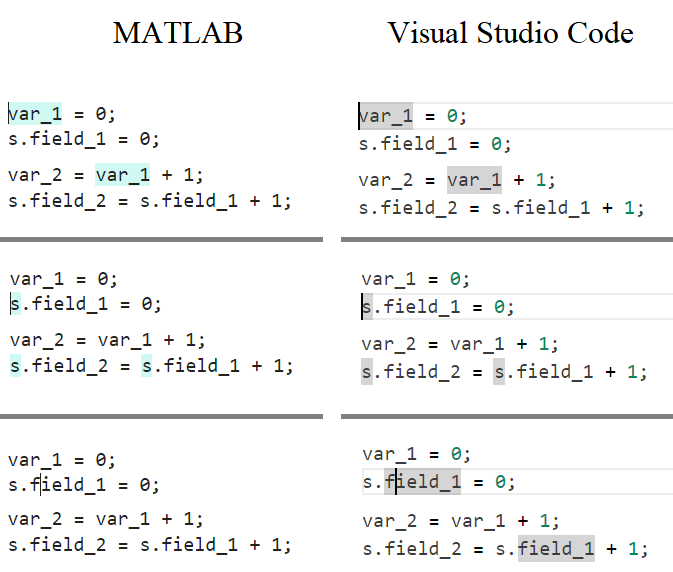
In the MATLAB editor, when clicking on a variable name, all the other instances of the variable name will be highlighted.
But this does not work for structure fields, which is a pity. Such feature would be quite often useful for me.
I show an illustration below, and compare it with Visual Studio Code that does it. ;-)
I am using MATLAB R2023a, sorry if it has been added to newer versions, but I didn't see it in the release notes.
Dear members, I’m currently doing research on the subject of using Generative A.I. as a digital designer. What our research group would like to know is which ethical issues have a big impact on the decisions you guys and girls make using generative A.I.
Whether you’re using A.I. or not, we would really like to know your vision and opinion about this subject. Please empty your thoughts and oppinion into your answers, we would like to get as much information as possible.
Are you currently using A.I. when doing your job? Yes, what for. No (not yet), why not?
Using A.I., would you use real information or alter names/numbers to get an answer?
What information would or wouldn’t you use? If the client is asking/ordering you to do certain things that go against your principles, would you still do it because order is order? How far would you go?
Who is responsible for the outcome of the generated content, you or the client?
Would you still feel like a product owner if it was co-developed with A.I.?
What we are looking for is that we would like to know why people do or don’t use AI in the field of design and wich ethical considerations they make. We’re just looking for general moral line of people, for example: 70% of designers don’t feel owner of a design that is generated by AI but 95% feels owner when it is co-created.
So therefore the questions we asked, we want to know the how you feel about this.

Welcome to MATLAB Central's first Ask Me Anything (AMA) session! Over the next few weeks, I look forward to addressing any questions or curiosities you might have about MATLAB, the forum, sasquatches, or whatever's on your mind. Having volunteered as a contributor to this community before joining MathWorks, I'm excited to act as a bridge between these two worlds. Let's kick things off by sharing a little-known fact about the forum’s staff contributors!
A couple of years ago, before I joined MathWorks as a developer on the Graphics and Charting team, I often wondered who were the MathWorkers with the [staff] moniker answering questions in the Answers forum. Is their MATLAB Central activity part of their day-to-day job expectations? Do they serve specific roles on some kind of community outreach team? Is their work in the forum voluntary in the same way that non-staff contributors volunteer their time?
Now that I'm on the inside, I'd like to share a secret with my fellow MATLAB users and MATLAB Central enthusiasts: with the exception of the MathWorks Support Team, staff participation in the Answers forum is completely voluntary! The staff contributions you see in the forum arise from pure intrinsic motivation to connect with users, help people out of ruts, and spread the word about our product!
For example, Steven Lord has contributed 20-150 answers per month for 9 years! Steven is a quality engineer for core MATLAB numerical functions. Cris LaPierre develops training material and has been a faithful contributor in the forum for almost 6 years! Kojiro Saito and Akira Agata have been tackling Japanese content for more than 7 years! There are many others who have inspired me as a user, and I am honored to now call colleagues: Peter Perkins, Michio, Joss Knight, Alan Weiss, Jiro Doke, Edric Ellis, and many others who deserve appreciation.
The forum's success hinges on the invaluable contributions from the majority of non-staff volunteers, whose dedication and expertise fuel our community. But I know I wasn't alone in wondering about these staff contributors, so now you're in on the secret!
I'm curious to know what other topics you're interested in learning about. Ask me anything!
Temporary print statements are often helpful during debugging but it's easy to forget to remove the statements or sometimes you may not have writing privileges for the file. This tip uses conditional breakpoints to add print statements without ever editing the file!
What are conditional breakpoints?
Conditional breakpoints allow you to write a conditional statement that is executed when the selected line is hit and if the condition returns true, MATLAB pauses at that line. Otherwise, it continues.
The Hack: use ~fprintf() as the condition
fprintf prints information to the command window and returns the size of the message in bytes. The message size will always be greater than 0 which will always evaluate as true when converted to logical. Therefore, by negating an fprintf statement within a conditional breakpoint, the fprintf command will execute, print to the command window, and evalute as false which means the execution will continue uninterupted!
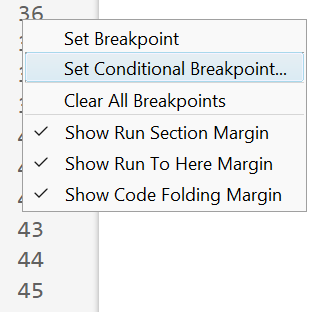
How to set a conditional break point
1. Right click the line number where you want the condition to be evaluated and select "Set Conditional Breakpoint"
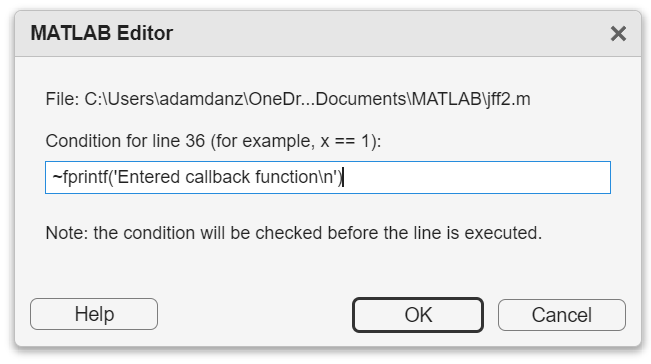
2. Enter a valid MATLAB expression that returns a logical scalar value in the editor dialog.
Handy one-liners
Check if a line is reached: Don't forget the negation (~) and the line break (\n)!
~fprintf('Entered callback function\n')
Display the call stack from the break point line: one of my favorites!
~fprintf('%s\n',formattedDisplayText(struct2table(dbstack)))
Inspect variable values: For scalar values,
~fprintf('v = %.5f\n', v)
~fprintf('%s\n', formattedDisplayText(v)).
Make sense of frequent hits: In some situations such as responses to listeners or interactive callbacks, a line can be executed 100s of times per second. Incorporate a timestamp to differentiate messages during rapid execution.
~fprintf('WindowButtonDownFcn - %s\n', datetime('now'))
Closing
This tip not only keeps your code clean but also offers a dynamic way to monitor code execution and variable states without permanent modifications. Interested in digging deeper? @Steve Eddins takes this tip to the next level with his Code Trace for MATLAB tool available on the File Exchange (read more).
Summary animation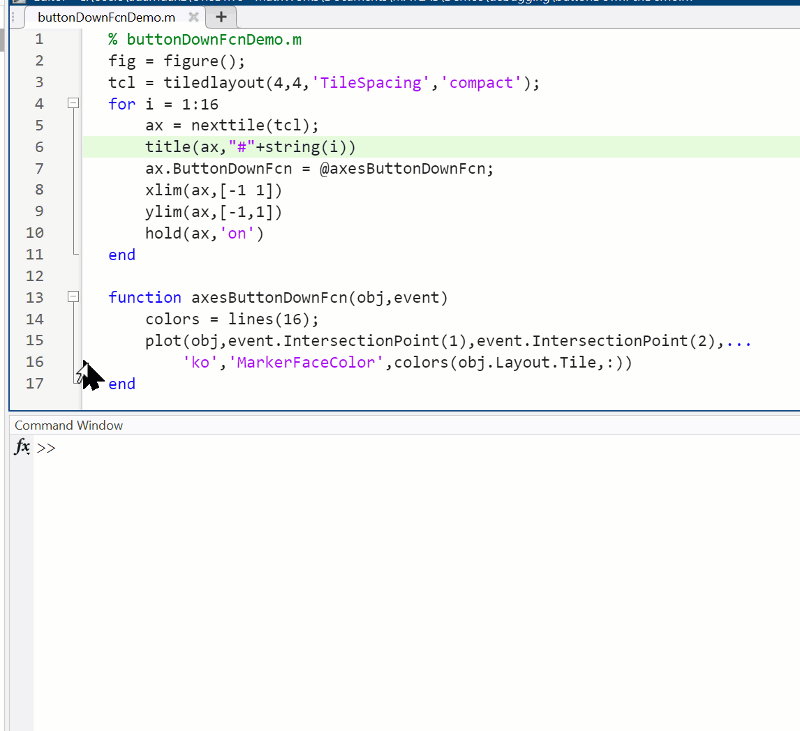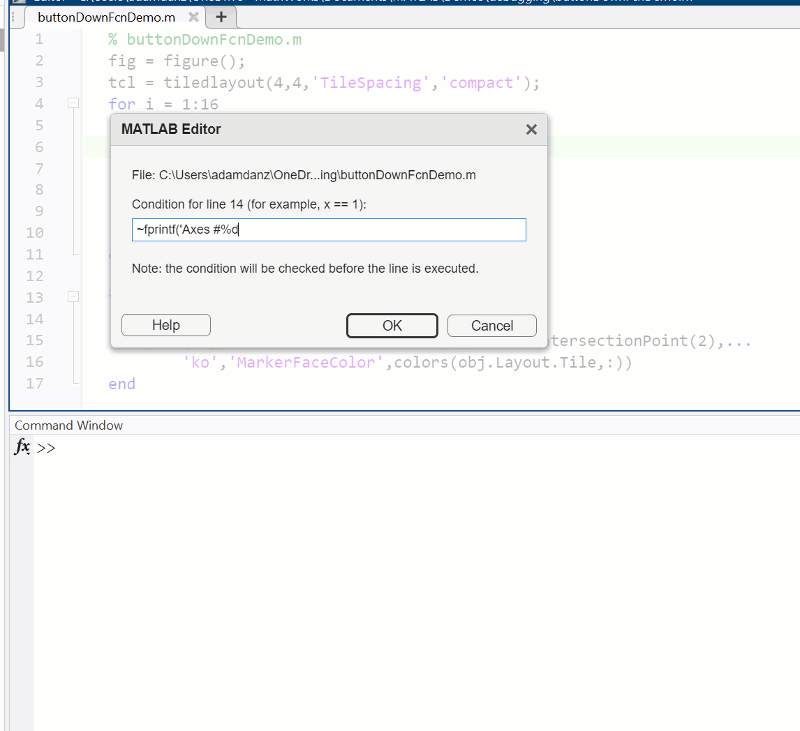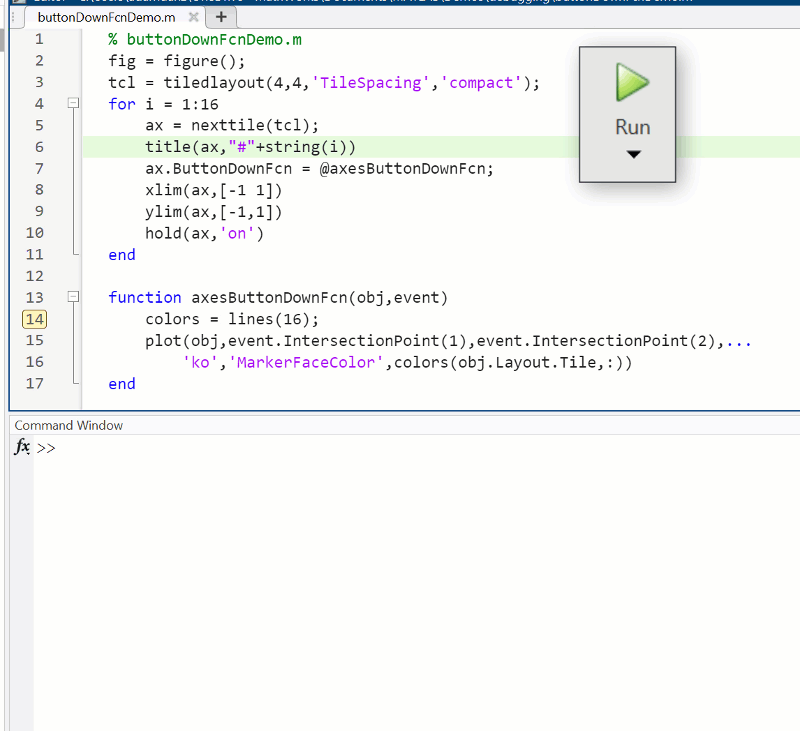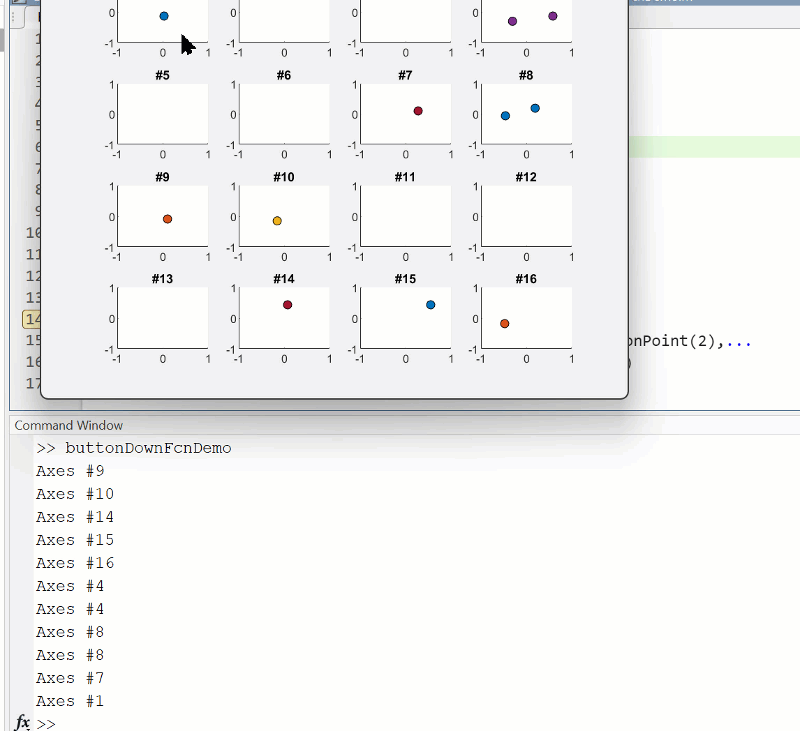

To reproduce the events in this animation:
% buttonDownFcnDemo.m
fig = figure();
tcl = tiledlayout(4,4,'TileSpacing','compact');
for i = 1:16
ax = nexttile(tcl);
title(ax,"#"+string(i))
ax.ButtonDownFcn = @axesButtonDownFcn;
xlim(ax,[-1 1])
ylim(ax,[-1,1])
hold(ax,'on')
end
function axesButtonDownFcn(obj,event)
colors = lines(16);
plot(obj,event.IntersectionPoint(1),event.IntersectionPoint(2),...
'ko','MarkerFaceColor',colors(obj.Layout.Tile,:))
end
numel(v)
6%
length(v)
13%
width(v)
14%
nnz(v)
8%
size(v, 1)
27%
sum(v > 0)
31%
2537 个投票
As far as I know, the MATLAB Community (including Matlab Central and Mathworks' official GitHub repository) has always been a vibrant and diverse professional and amateur community of MATLAB users from various fields globally. Being a part of it myself, especially in recent years, I have not only benefited continuously from the community but also tried to give back by helping other users in need.
I am a senior MATLAB user from Shenzhen, China, and I have a deep passion for MATLAB, applying it in various scenarios. Due to the less than ideal job market in my current social environment, I am hoping to find a position for remote support work within the Matlab Community. I wonder if this is realistic. For instance, Mathworks has been open-sourcing many repositories in recent years, especially in the field of deep learning with typical applications across industries. I am eager to use the latest MATLAB features to implement state-of-the-art algorithms. Additionally, I occasionally contribute through GitHub issues and pull requests.
In conclusion, I am looking forward to the opportunity to formally join the Matlab Community in a remote support role, dedicating more energy to giving back to the community and making the world a better place! (If a Mathworks employer can contact me, all the better~)
We're thrilled to unveil a new feature in the MATLAB Central community: User Following.
Our community is so lucky to have many experienced MATLAB experts who generously share their knowledge and insights across different applications, including Answers, File Exchange, Discussions, Contests, or Blogs.
With the introduction of User Following feature, you can now easily track new content across different areas and engage in discussions with people you follow. Simply click the ‘Follow’ button located on their profile page to start.
Depending on your communication setting, you will receive notifications via email and/or view updates in your ‘Followed Activity’ feeds. To tailor your feed, select the ‘People’ filter and focus on activities from those you follow.
We strongly encourage you to take advantage of the User Following feature to foster learning and collaboration within our vibrant community.
Who will be the first person you choose to follow? Share your answer in the comments section below and let's inspire each other to explore new horizons together.
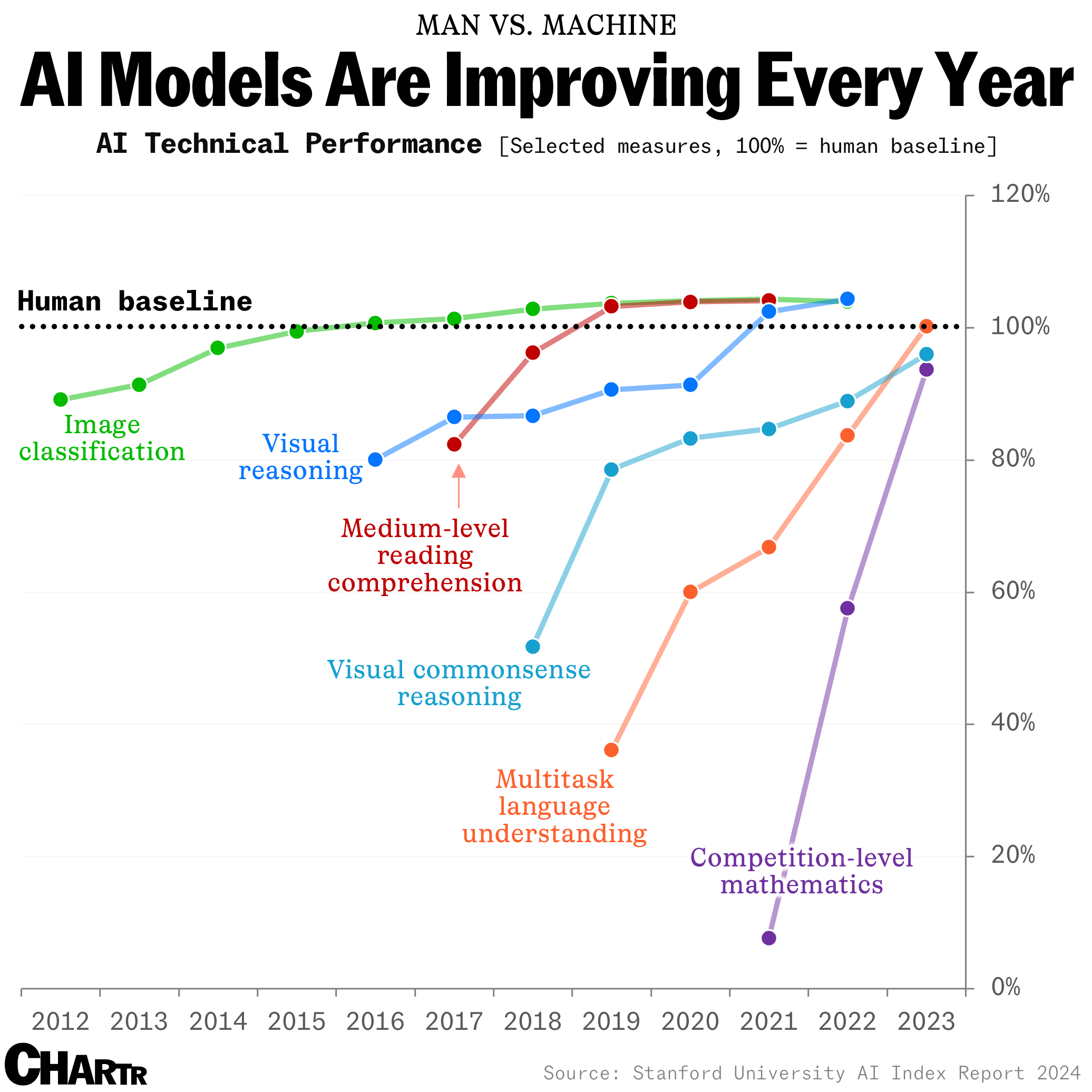
How long until the 'dumbest' models are smarter than your average person? Thanks for sharing this article @Adam Danz
ismissing( { [ ] } )
26%
ismissing( NaN )
18%
ismissing( NaT )
11%
ismissing( missing )
21%
ismissing( categorical(missing) )
9%
ismissing( { '' } ) % 2 apostrophes
16%
896 个投票
I created an ellipse visualizer in #MATLAB using App Designer! To read more about it, and how it ties to the recent total solar eclipse, check out my latest blog post:
Github Repo of the app (you can open it on MATLAB Online!):